Pa led na Arktiku je morski led, njegove topljenje ne utice i ne moze po fizici, da utice na dizanje nivoa mora.
O ledu koji je vec u vodi i negovom (ne)efektu na podizanja nivoa vode.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aOCqHRpQh88Temperatura u zadnjih 100tinak godina
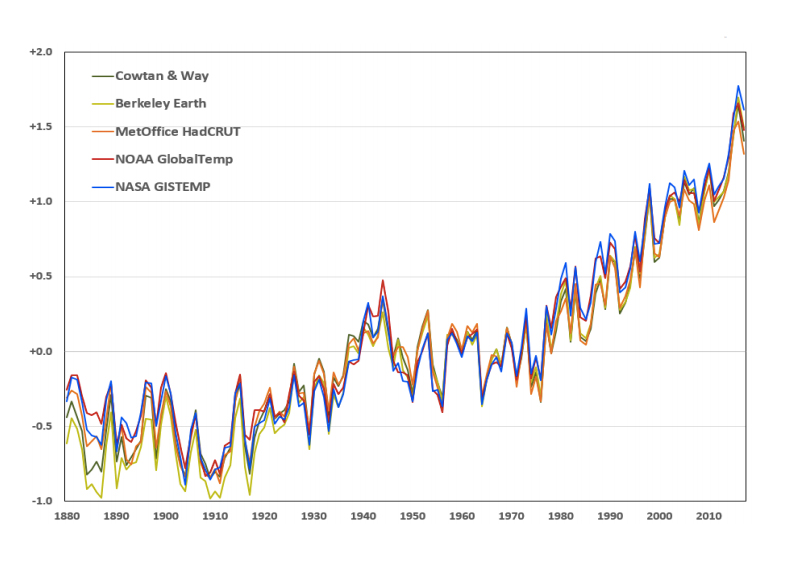
A mora rastu vec hiljadama godinama, i rasce (i padati) dok god ima leda, tj. dok god smo "ledenom" periodu.

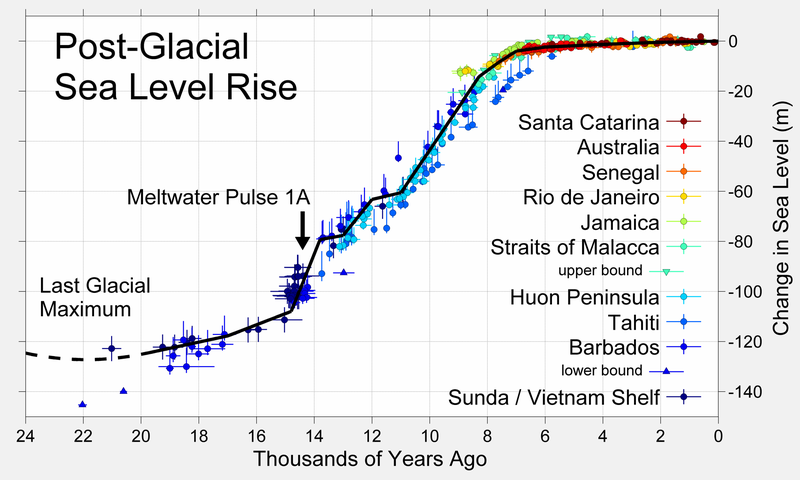
Nije nista cudno sto mora rastu, da neko ne pomisli, kao ni u celom zagrevanju zemlje. Stvar je samo u brzini porasta temperature i u tome sta je uzrokuje, odnosno da li je covekov uticaj ili ne. Tu ima podeljenih misljenja. Inace o porastu mora i "ledenom dobu": Mi smo trenutno u interglacijalu glacijala, tj. toploj fazi ledenog doba. Evo tekst o zelenoj vs ledenoj zemlji kroz istoriju, i nedetaljna "slika", tako da bi ja i vecina ljudi mogli da razumemo.
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
Greenhouse Earth
Overview of greenhouse EarthA "greenhouse Earth" or "hothouse Earth" is a period in which
there are no continental glaciers whatsoever on the planet, the levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (such as water vapor and methane) are high, and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) range from 28 °C (82.4 °F) in the tropics to 0 °C (32 °F) in the polar regions.
The Earth has been in a greenhouse state for about 85% of its history.This state should not be confused with a hypothetical hothouse earth, which is an irreversible tipping point corresponding to the ongoing runaway greenhouse effect on Venus. The IPCC states that "a 'runaway greenhouse effect'—analogous to [that of] Venus—appears to have virtually no chance of being induced by anthropogenic activities."
Causes of greenhouse EarthThere are several theories as to how a greenhouse Earth can come about. The geological record shows CO2 and other greenhouse gases are abundant during this time. Tectonic movements were extremely active during the more well-known greenhouse ages (such as 368 million years ago in the Paleozoic Era). Because of continental rifting (continental plates moving away from each other) volcanic activity became more prominent, producing more CO2 and heating up the Earth's atmosphere.
Earth is more commonly placed in a greenhouse state throughout the epochs, and the Earth has been in this state for approximately 80% of the past 500 million years, which makes understanding the direct causes somewhat difficult.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_____
Icehouse Earth
Ice age and Timeline of glaciation
Overview of icehouse EarthAn "icehouse Earth" is the earth as it experiences an ice age.
Unlike a greenhouse Earth, an icehouse Earth has ice sheets present, and these sheets wax and wane throughout times known as glacial periods and interglacial periods. During an icehouse Earth, greenhouse gases tend to be less abundant, and temperatures tend to be cooler globally.
The Earth is currently in an icehouse stage, as ice sheets are present on both poles and glacial periods have occurred at regular intervals over the past million years.
Causes of icehouse EarthThe causes of an icehouse state are much debated, because not much is really known about the transitions between greenhouse and icehouse climates and what could make the climate change. One important aspect is clearly the decline of CO2 in the atmosphere, possibly due to low volcanic activity.
Other important issues are the movement of the tectonic plates and the opening and closing of oceanic gateways. These seem to play a crucial part in icehouse Earths because they can bring cool waters from very deep water circulations that could assist in creating ice sheets or thermal isolation of areas. Examples of this occurring are the opening of the Tasmanian gateway 36.5 million years ago that separated Australia and Antarctica and which is believed to have set off the Cenozoic icehouse, and the creation of the Drake Passage 32.8 million years ago by the separation of South America and Antarctica, though it was believed by other scientists that this did not come into effect until around 23 million years ago. The closing of the Isthmus of Panama and the Indonesian seaway approximately 3 or 4 million years ago may have been a major cause for our current icehouse state. For the icehouse climate, tectonic activity also creates mountains, which are produced by one continental plate colliding with another one and continuing forward. The revealed fresh soils act as scrubbers of carbon dioxide, which can significantly affect the amount of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. An example of this is the collision between the Indian subcontinent and the Asian continent, which created the Himalayan Mountains about 50 million years ago.
Glacials and interglacials Glacial period and InterglacialWithin icehouse states, there are "glacial" and "interglacial" periods that cause ice sheets to build up or retreat. The causes for these glacial and interglacial periods are mainly variations in the movement of the earth around the Sun. The astronomical components, discovered by the Serbian geophysicist Milutin Milanković and now known as Milankovitch cycles, include the axial tilt of the Earth, the orbital eccentricity (or shape of the orbit) and the precession (or wobble) of the Earth's spin. The tilt of the axis tends to fluctuate between 21.5° to 24.5° and back every 41,000 years on the vertical axis. This change actually affects the seasonality upon the earth, since more or less solar radiation hits certain areas of the planet more often on a higher tilt, while less of a tilt would create a more even set of seasons worldwide. These changes can be seen in ice cores, which also contain information showing that during glacial times (at the maximum extension of the ice sheets), the atmosphere had lower levels of carbon dioxide. This may be caused by the increase or redistribution of the acid/base balance with bicarbonate and carbonate ions that deals with alkalinity.
During an icehouse, only 20% of the time is spent in interglacial, or warmer times.Model simulations suggest that the current interglacial climate state will continue for at least another 100,000 years, due to CO2 emissions - including complete deglaciation of the Northern Hemisphere.
Inace tekstovi su sa Wikipedie, izvinjavam sa na malo nabacanom, ali NG je, nisam imao vise vremena hehe.